Cybersecurity and IoT security breaches are top trending topics in the modern automated and digitised work environments. It could be due to the ever-increasing number of online threats and attacks since the pandemic started.
IoT cyber attacks have more than doubled year-on-year during the first half of 2021, according to anti-virus and computer security service provider Kaspersky. From January to June this year, some 1.51 billion breaches of Internet of Things (IoT) devices took place, an increase from 639 million in 2020.
Is your business equipped and protected from any potential threats? Here are a few things to consider when it comes to IoT Security:
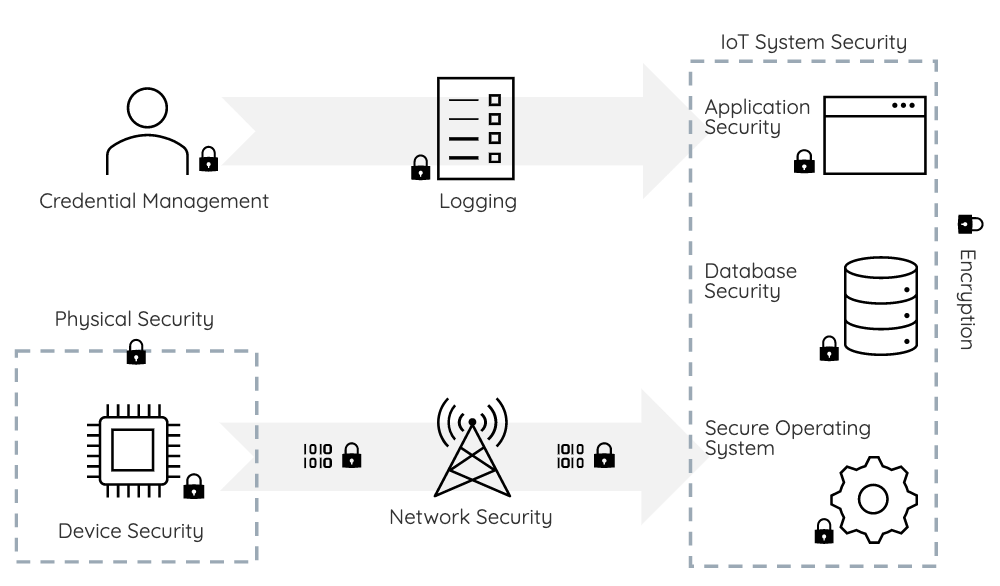
1. Physical Security
It is important that Production equipment is protected against physical access to its data and intellectual property. This is done by physically barring access and removing all means of unwanted connections.
2. Device Security
Minimise the risk of rogue code being run at boot time by checking devices for a staged boot sequence. Every stage should be checked for validity before initialising.
3. Secure Operating System
Are your operating systems up to date? Protect your operating system against future security threats by always using the latest software. Removing all unnecessary access rights and functions, and limiting the visibility of the system reduces the security vulnerabilities further.
4. Application Security
Security must always be designed from the outset and not added on as an afterthought! Documentation of security design ensures subsequent issues can be more readily addressed when required. However, older applications may require redesigning.
5. Database Security
Most modern databases offer a range of encryption methods, however databases should also contain all device interactions and related data for security analysis and auditing purposes.
6. Credential Management
Control the identities of people, devices, or other entities to prevent them from gaining unauthorised access to data or services. Make sure passwords, encryption keys, digital certificates and other credential data is handled securely and updated periodically.
7. Logging
Access and Event logging is vital for aiding fault and security management. Ensure that System and Access logs are maintained and should only be made available for inspection by personnel with authorised and approved security clearance.
8. Encryption
Any data attributable to an individual should be encrypted to ensure privacy and comply with data protection regulations. All management data must be encrypted to protect the integrity and availability of the service.
9. Network Connections
To protect points of access, limitations need to be put into place to minimise possible access routes to the device. It is also vital to ensure the device only makes connections it specifically requires for functioning and that any sensitive data (e.g., keys, personal data, passwords) exchanged over those connections are kept secret.
10. Security Compliance
A further area to consider is compliance against certain security standards. Some of the standards to consider include ISO27001, ISO/IEC 27002, NIST SP800-53, ISO45001, FISC, HDS, HIPAA, ISO 4001, ISO 22301, ISO 27001, ISO 50001, ISO 9001.
How to address security issues
Committing towards secure IoT infrastructure and ecosystem may seem like going down a rabbit hole, however due to the nature of our new digitised environments it becomes a necessity as well as a legal requirement. Adopting security does not have to be as challenging as it seems; contact us for see how our services in Cybersecurity and IoT can simplify these challenges.